Congratulation guys for making it this far in our journey to become a full-stack web developer.

Today's topic is Objects in JS.
Before understanding the objects let's deep dive into the limitation of the array:-
let's understand it by an example:
Rahul is a user of your website and you need to store his data such as name, email, password, and mobile.
we can add this data to the array as follows
let users= ['name','email','password','mobile']
let data = ['Rahul','rahul@gmail.com','*45Aedas',9641851224]
Suppose now I need to find the password of Rahul, for that first we need to find the index of the password in the employees' array, and then from that index, we can find the password of Rahul.
But is it a good approach?
Suppose a company has 5000 users and we store their data in such a
To address such situations objects were introduced.
What is an Object?
An object is a collection of key-value pairs. The keys are also known as properties, and the values can be any data type, including strings, numbers, arrays, or even other objects.
How to declare an Object?
var details={}
in object the data are stored in key-value pairs
const person = {
name: "John",
age: 30,
job: "software developer",
hobbies: ["reading", "swimming"]
};
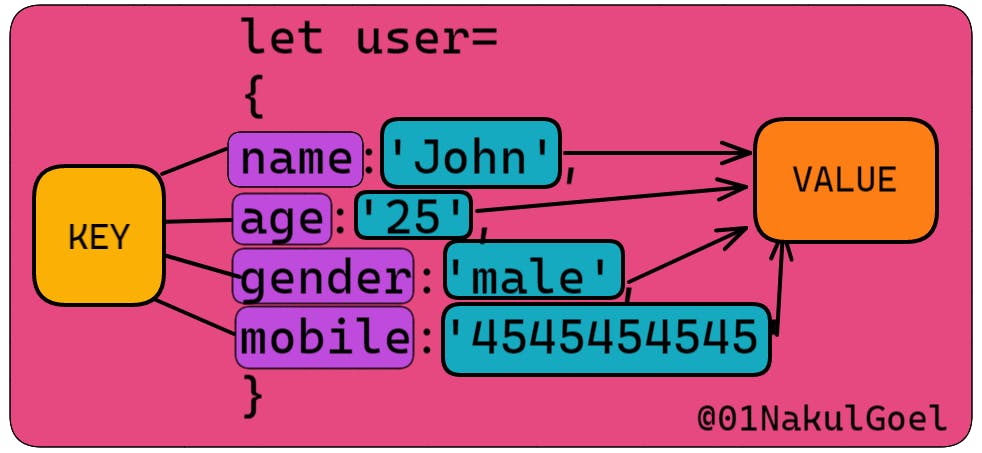
Properties of object
Accessing the value
Dot Notation
Syntax
object.keyconst person = { name: "John", age: 30, job: "software developer", hobbies: ["reading", "swimming"] }; person.name //John person.age //30 person.job //software developer person.hobbies // ["reading", "swimming"] person.hobbies[0] // readingBracket Notation
Syntax
object["key"]const person = { name: "John", age: 30, job: "software developer", hobbies: ["reading", "swimming"] }; person['name'] //John person['age'] //30 person['job'] //software developer person['hobbies'] // ["reading", "swimming"] person['hobbies'][0] // readingAdding new key
Dot Notation
object.key=value var employees = { Rahul:'1,00,000', Suraj:'4,00,000', Ashutosh:'5,00,000', John:'1,00,000' } //To add new employee we can do employees.Nishant='2,00,000' console.log(employees) /*{Ashutosh: "5,00,000". John: "1,00,000", Nishant: "2,00,000", Rahul: "1,00,000", Suraj: "4,00,000"}*/Bracket Notation
object['key']=value var employees = { Rahul:'1,00,000', Suraj:'4,00,000', Ashutosh:'5,00,000', John:'1,00,000' } //To add new employee we can do employees['Nishant']='2,00,000' console.log(employees) /*{Ashutosh: "5,00,000". John: "1,00,000", Nishant: "2,00,000", Rahul: "1,00,000", Suraj: "4,00,000"}*/
Deleting a key
var employees = { Rahul:'1,00,000', Suraj:'4,00,000', Ashutosh:'5,00,000', John:'1,00,000' } delete employees.Rahul // it will delete rahul key delete employees['Suraj'] // it will delete rahul key
loops in object
The object cannot be iterated with a normal for loop as an object doesn't have an index as numbers. so to iterate objects we have a special loop that is for in loop.
const person = {
name: "John",
age: 30,
job: "software developer",
hobbies: ["reading", "swimming"]
};
for(let key in person){
// Keep in mind here you need to use box notation.
// also do console.log(key)
console.log(person[key])
}
Arrays Inside Object
we can store an array inside objects as well.
let detail = {
title: "FB 3-Day: 3 Workouts Per Week for 2 Weeks",
price: "7.99",
difficultyLevel: [ 3,4],
bodyFocus: "Total Body",
equipmentData: ["Dumbbell", "Mat" ],
trainingTypeData: ["Strength Training"]}
as in the above example, we have stored an array in an object.
we can store any data structure and data type as a value in an object such as a number, boolean, string, bigInt, array, and object as well.
Even we can store functions as well in the value part which we will learn about in the next session.
The object inside the object (Nested Object)
let school = {
class11: {
rahulMarks: { english: 99, hindi: 100, maths: 70 },
},
};
// to access the marks of english
school['class11']['rahulMarks']['english']
Assignment
create an object with five names as keys and give them a value.
print all the keys using for in loop.
You are given a variable
let str='asdnbknsadknsadnjk'To make an object using a loop that will give the key as the character and the value as a number of characters.
Sample Input
let str='saaslaa'
Sample output
{a:4,s:2,l:1}
Write a function
countPropertiesthat takes an object as an argument and returns the number of properties (key-value pairs) in the object.Write a function
getPropertyNamesthat takes an object as an argument and returns an array of all the property names (keys) in the object.Write a function
getPropertyValuesthat takes an object as an argument and returns an array of all the property values (values) in the object.Write a function
sumValuesthat takes an object as an argument and returns the sum of all the values in the object.Write a function
averageValuethat takes an object as an argument and returns the average of all the values in the object.Write a function
findLargestValuethat takes an object as an argument and returns the largest value in the object.Write a function
findSmallestValuethat takes an object as an argument and returns the smallest value in the object.Write a function
reversePropertiesthat takes an object as an argument and returns a new object with the keys and values reversed (i.e. the keys become the values and the values become the keys).Write a function
findLongestKeythat takes an object as an argument and returns the longest property name (key) in the object.Write a function
swapPropertiesthat takes an object as an argument and returns a new object with the keys and values of the original object swapped (i.e. the values become the keys and the keys become the values).