Hi, I am Nakul Goel and I will be your instructor in this 8 weeks react mastery course, where we will be covering everything about react.
This course is entirely free for all students who want to learn.
In this course, we will be going from beginner level to all the way to mastering react, so this is friendly for beginners but keep in mind this course has some prerequisites.
so please check all the prerequisites and then only start this course.
Pre-Requisite
Learn HTML and CSS.
Learn JavaScript and be familiar with ES6 syntax.
Basic understanding of DOM (document object model).
Download and install a code editor.
My preference will be to download and install VS Code.
A quick guide to installing VS code:-
Go to the Visual Studio Code website (code.visualstudio.com)
Click the "Download" button on the homepage
Select the version of VS Code that you want to download (e.g. Windows, macOS, Linux)
Follow the prompts to complete the installation
Make an account on https://codepen.io/ and https://codesandbox.io/ because I will be sharing a lot of code on these platforms so be aware of these platforms.
Welcome Everyone, I am very happy you made it through, so congratulation.
The first 10 blogs of react can be tricky for most of you, so even if you are not completely understanding a part then also try to learn and complete at least 10 blogs after 10 blogs react will be super easy for all of you.
What is a framework and why do we need it?
A framework is a set of tools, libraries, and conventions that are designed to help developers build applications more efficiently.
It provides a structure that developers can follow, which helps them to avoid reinventing the wheel and to focus on building the unique features of their applications.
Imagine that you are planning a vacation. A framework is like a pre-planned tour package that includes everything you need for your trip. It includes a set of hotels, flights, and activities that are carefully selected and organized for you.
Without a framework, you would have to plan every aspect of your trip yourself. You would need to research and book your own flights, hotels, and activities, which can be time-consuming and overwhelming.
On the other hand, with a framework, you can simply follow the pre-planned itinerary and enjoy your trip without having to worry about the details. The framework takes care of everything for you, so you can focus on having a good time.
There are several benefits to using a framework:
Time savings: A framework can save developers time by providing pre-built libraries and tools that they can use in their applications. This means that they don't have to build everything from scratch, which can be time-consuming.
Consistency: A framework can help to ensure that an application is built in a consistent manner, which can make it easier to maintain and scale.
Best practices: A framework is often based on best practices that have been developed by experienced developers. This means that developers who use a framework can benefit from the collective knowledge and experience of the community.
Support: A framework often has a strong community of developers who can provide support and assistance when needed.
High Reusability and readability.
Why React Why not Angular or Vue?
React, Angular, and Vue.js are all popular JavaScript libraries for building user interfaces. They each have their own strengths and are suitable for different types of projects.
Angular is one of the best frameworks developed by google but it's very complex to understand, it has a wide range of tools to develop a web application, and it includes everything to build from the user side interface to the backend. it is used to build enterprise-level complex applications and the prerequisite to learn it will include typescript as well.
Full-featured framework
Large community
TypeScript support
MVC architecture
now let's talk about Vue, it's a lightweight framework developed by Evan You and is used to develop small-size applications.
Easy to learn
Lightweight and fast
Reactive components
Strong ecosystem
why I am telling you about angular or Vue that's because you should always be familiar with the present technologies.
Now it's time why react.
why are we learning react?
any idea?
This course is about react that's why we are learning react lol.
Why & What is React?
React is a popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces. It was developed by Facebook and is often used for building single-page applications and mobile applications.
some of the popular websites made using react framework are:-

Downloads of react, so you can automatically see how popular is react.

if we need to develop an android or ios app then we also have react native which is similar to react.

so there are a lot of things that we can do with react.
Remember react is built on top of js which means all the rules of JS are applied to react.
Here is an example that compares React and JavaScript using the metaphor of building a car:
- React is like the body of the car. It provides the structure and appearance of the car, but it doesn't do anything on its own.
JavaScript is like the engine of the car. It provides the power and functionality that makes the car move.

Let's revise some of the basic ES6 syntaxes so that we can become more powerful:-
Arrow functions: Arrow functions are a shorter syntax for defining functions.
Arrow functions are anonymous, which means that they don't have a name.
Arrow functions do not have their own
thisvalue. Instead, they inherit thethisvalue from the surrounding context.Arrow functions cannot be used as constructors (i.e., you cannot use
newan arrow function)
For example, you can use an arrow function like this:
```javascript
const greet = name => `Hello, ${name}!`;
const hello = (name,place)=>{
`Hello, ${name} from ${place}`
}
```
- Destructuring: Destructuring allows you to extract values from objects and arrays and assign them to variables. For example, you can use destructuring like this:
const user = { name: 'John', age: 30 };
const { name, age } = user;
Spread operator: The spread operator allows you to expand an array or object into separate elements or properties. For example, you can use the spread operator like this:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3]; const newNumbers = [...numbers, 4, 5];Classes: ES6 introduces a new syntax for defining classes. For example, you can define a class like this:
class Animal { constructor(name) { this.name = name; } speak() { console.log(`${this.name} makes a sound.`); } } const dog = new Animal('Dog'); dog.speak(); // Output: "Dog makes a sound."template strings: Template strings are a new way to create strings that support interpolation and multi-line strings. For example, you can use template strings like this:
const name = 'John';
console.log(`Hello, ${name}!`); // Output: "Hello, John!"
const multiline = `This is a
multiline string.`;
console.log(multiline); // Output: "This is a\nmultiline string."
Immutability and Mutability:-
Immutability refers to the idea that once an object is created, its properties cannot be changed. In other words, an immutable object is an object that is read-only.
in JavaScript, immutability can be achieved by using a combination of const declarations, object.freeze(), and the spread operator (...).
const user = { name: 'John', age: 30 }; // Freeze the object to prevent further changes Object.freeze(user); // This will throw an error because the object is frozen try { user.name = 'Jane'; } catch (e) { console.log(e); } // Create a new object with the updated name using the spread operator const updatedUser = { ...user, name: 'Jane' }; console.log(user.name); // Output: "John" console.log(updatedUser.name); // Output: "Jane"Default parameters: ES6 allows you to specify default values for function parameters. For example, you can use default parameters like this:
const greet = (name = 'John') => `Hello, ${name}!`;
console.log(greet()); // Output: "Hello, John!"
console.log(greet('Jane')); // Output: "Hello, Jane!"
Modules: ES6 introduces a new syntax for organizing code into modules. For example, you can define a module like this:
// Define a module in a file called "math.js" export const add = (x, y) => x + y; export const subtract = (x, y) => x - y; // Import the module in another file import { add, subtract } from './math'; console.log(add(1, 2)); // Output: 3 console.log(subtract(5, 3)); // Output: 2Spread and rest operator: The spread operator allows you to expand an array or object into separate elements or properties, while the rest operator allows you to capture multiple arguments into an array. For example, you can use the spread and rest operator like this:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3]; const newNumbers = [...numbers, 4, 5]; console.log(newNumbers); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] const sum = (...args) => args.reduce((acc, val) => acc + val, 0); console.log(sum(1, 2, 3)); // Output: 6Sets: Sets are a new data structure that allows you to store unique values. For example, you can use sets like this:
javascript const set = new Set([1, 2, 3]); set.add(4); set.delete(2); console.log(set.has(2)); // Output: false console.log(set.size); // Output: 3
- Higher Order Functions: It is a function that takes another function as an argument and returns a new function.
```javascript javascript const withLogging = (fn) => { return (...args) => { console.log('Calling function:', fn.name); return fn(...args); }; };
const add = (a, b) => a + b;
const addWithLogging = withLogging(add);
console.log(addWithLogging(1, 2)); // Output: 3 (with log message)
javascript //reduce HOF const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const sum = numbers.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue, 0);
console.log(sum); // Output: 10
//filter HOF const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const evenNumbers = numbers.filter(number => number % 2 === 0);
console.log(evenNumbers); // Output: [2, 4]
// Sort HOF const numbers = [4, 2, 5, 1, 3];
const sortedNumbers = numbers.sort((a, b) => a - b);
console.log(sortedNumbers); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
// map const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const doubledNumbers = numbers.map(number => number * 2);
console.log(doubledNumbers); // Output ```
Closures are functions that have access to the variables in the scope in which they were created, even if the function is called outside of that scope. Closures are a powerful feature in JavaScript and are often used to create functions with private variables or to create functions that have access to variables that are defined in outer scopes.
Promises are a pattern in JavaScript for handling asynchronous operations. A promise represents the result of an asynchronous operation, which may be a value or an error. Promises allow you to chain asynchronous operations together and to write asynchronous code in a more synchronous-looking style.
Async functions are a pattern in JavaScript for writing asynchronous code in a synchronous-looking style. An async function is a function that is marked with the
asynckeyword and returns a promise. Async functions can be used with theawaitoperator to wait for the promise to be resolved before continuing.The
GET,POST,PUT,PATCH, andDELETEHTTP methods are used to request data from or make changes to a server.GETis used to retrieve data,POSTis used to create data,PUTis used to update data,PATCHis used to partially update data, andDELETEis used to delete data. These methods are often used in combination with APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to interact with servers and databases.JSON Server is a tool that allows you to create a fake REST API by creating a JSON file and running it as a server. It is often used for prototyping or for testing applications that need to interact with an API.
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules that define how two or more systems can communicate with each other. An API often exposes a set of endpoints that can be used to perform different operations, such as retrieving data or making changes to data.
CRUD operations are the basic operations that are performed on a database or an API. CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, and Delete, and these operations correspond to the ability to create new data, retrieve existing data, update existing data, and delete existing data.
I want you guys to understand all the concepts in deep because of that I tried to help you revise all the concepts again.
Now we will learn react
One important announcement
A driver does not know how a car is made but one thing that he knows is how to drive a car.
so instead of focusing on how react is made do focus on how to use it effectively.
Let's learn react
React is a javascript frontend framework that is used to design beautiful user interfaces.
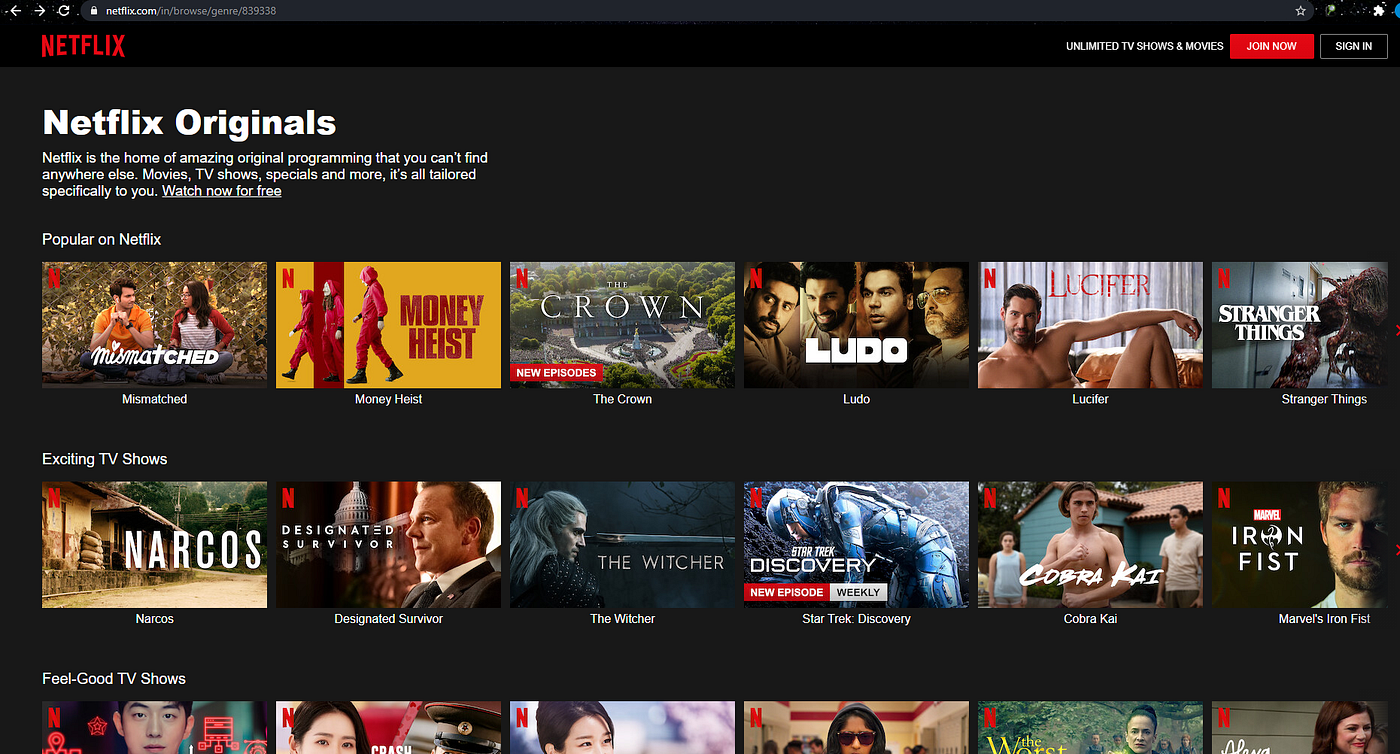
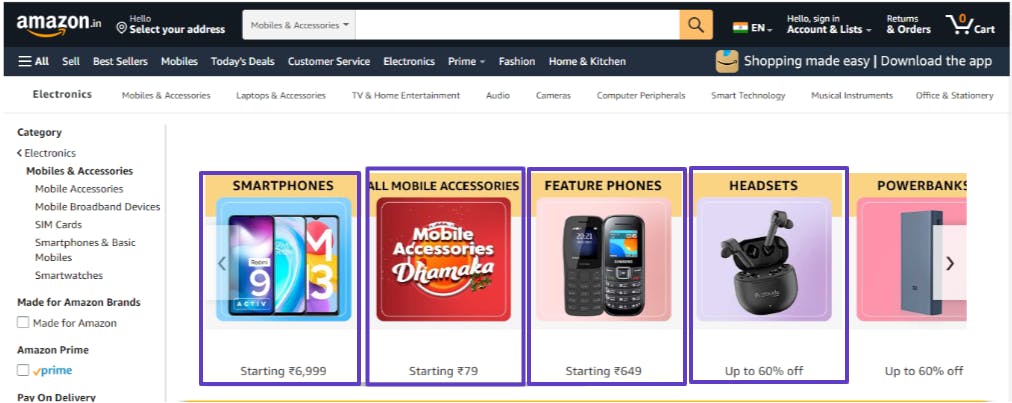
it increases the reusability of the same element again.
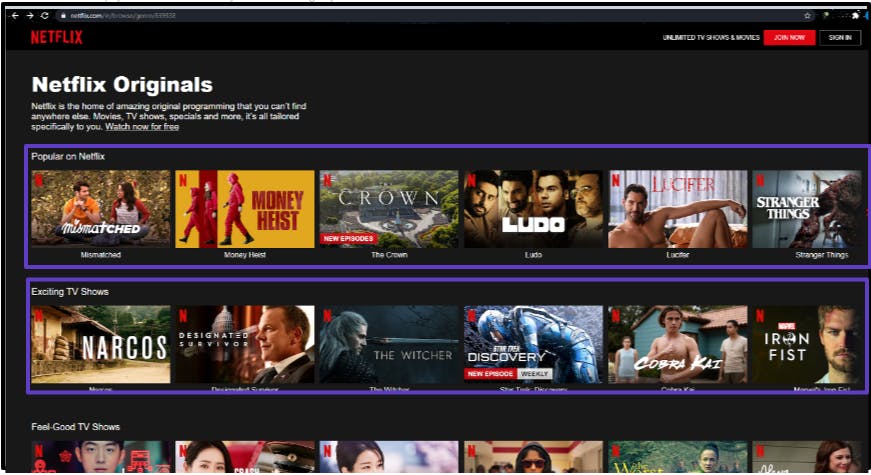
The above example is of the Twitter comment section where you can actually see a lot of common things, actually, everything is the same just the data changing, so all the comments in Twitter are not hardcoded all the code is dynamic.
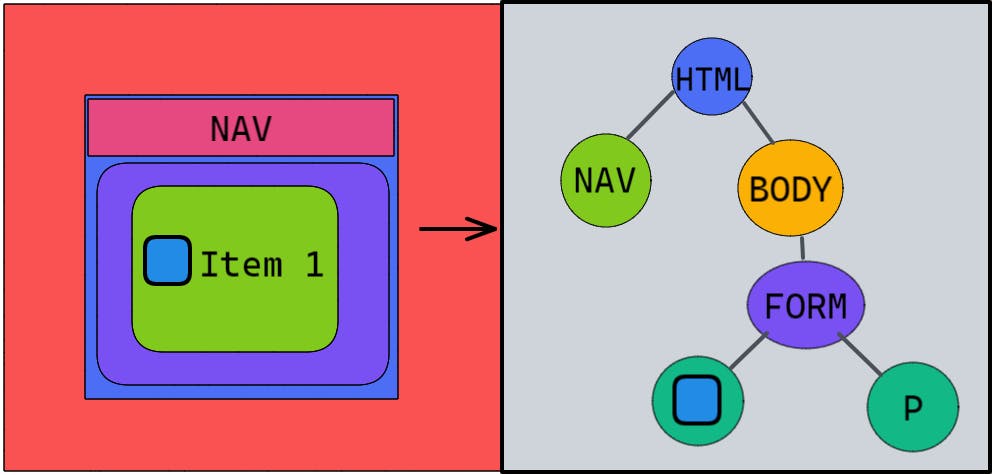
we can arrange a simple component of a form like this in the tree format.
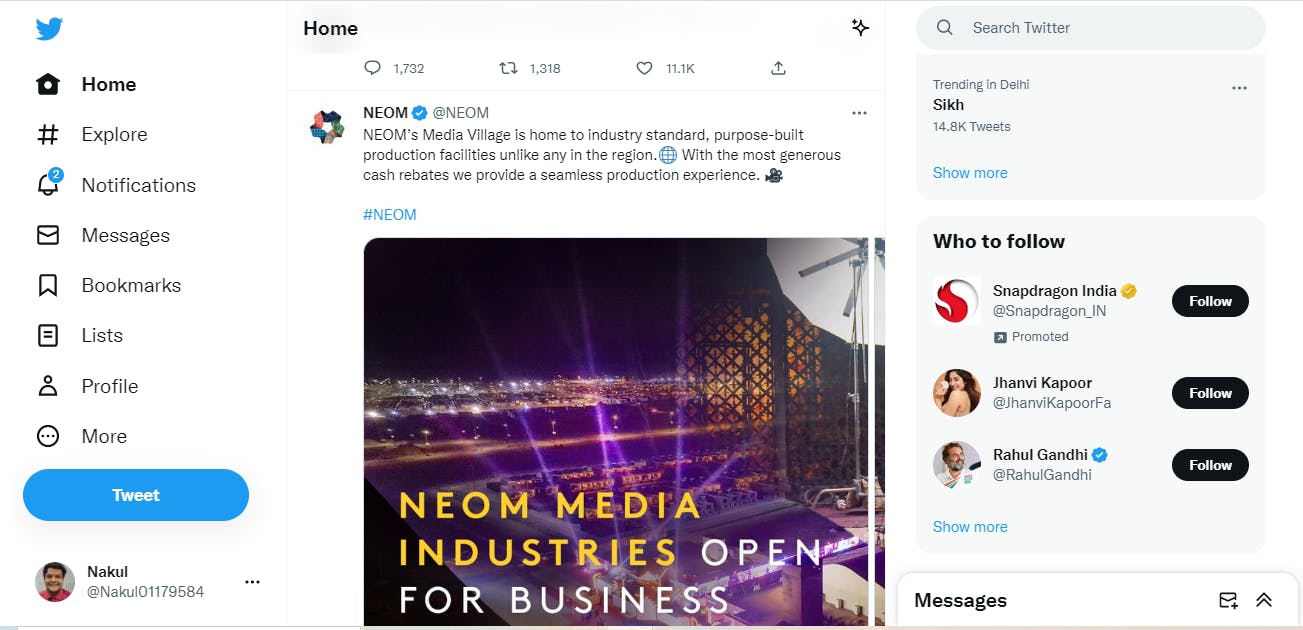
if i am searching or reloading this page then only the component inside home will change rest every component will remain still, this actually makes your application much faster.
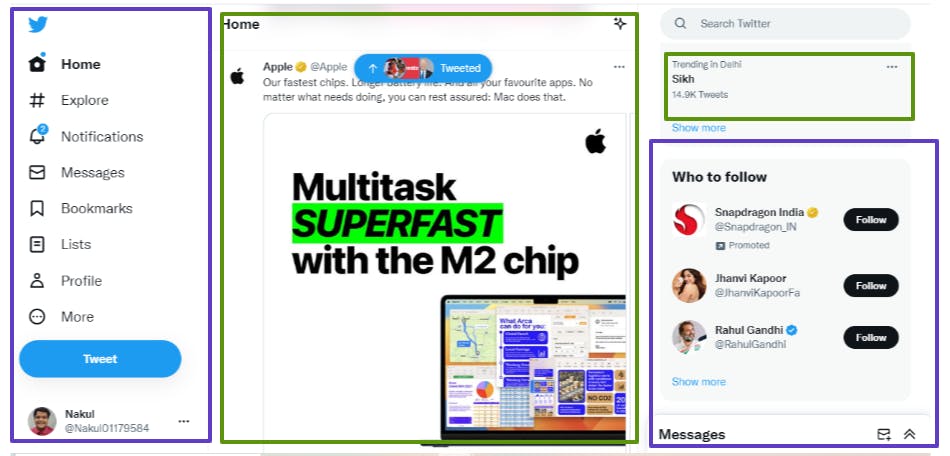
the green box actually changed and the purple remained the same. so instead of loading the whole page, only the required components were reloaded.
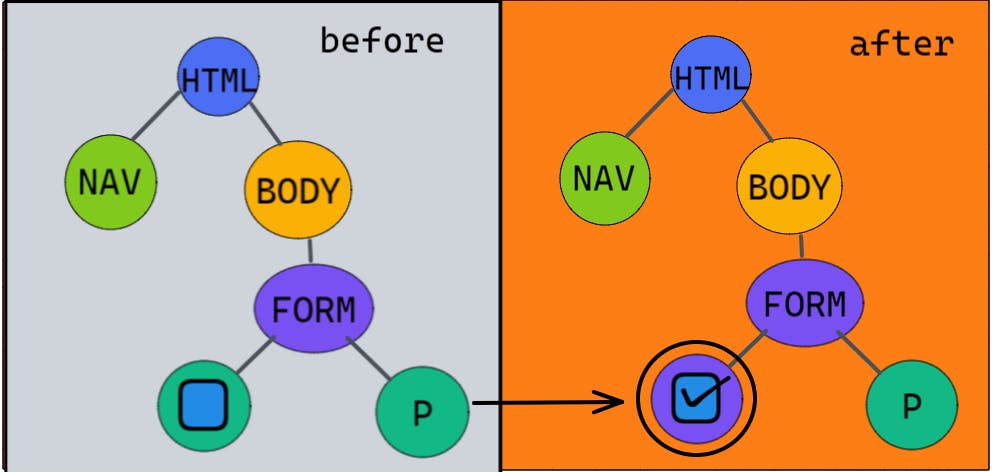
when there is a change instead of changing the whole virtual tree react compares the previous virtual tree with the current tree and calculate the minimum number of dom changes required. This step of updating the dom with a minimum number of updates is known as "reconciliation".
that's it for the introduction, we will meet in the next blog.
Keep Learning and do practice ES6.

