Hi, Hashnoders or Learners
today we will study some really amazing things about React.
in this blog, we will be doing some practice questions as well so tighten your seat belt as this journey will be a roller coaster ride for all of you.

React component?
In React, a component is a piece of reusable code that represents a part of a user interface. Components can be either based on functions or a class.
const MyCode = ()=>{
return(
<div>
<h1 style={{color:'red'}} >Nakul Goel</h1>
<p>I am learning React </p>
</div>
)
}
basically, (always remember to use PascalCase in React component) MyCode is a React component.
to render React component we will render it like the following part:-
root.render(
<MyCode />
)
we will always run react component as I have stated above.
In React Component, we can basically add an object that is a prop (short form for the properties ) to make it dynamic.
watch the below code
// props can be {style:"red",heading:"Nakul Goel",description:"I am learning react"}
const MyCode = (props)=>{
let {style,heading,description} = props
return(
<div>
<h1 style={style} >{heading}</h1>
<p> {description} </p>
</div>
)
}
here we are destructuring the props, I hope you guys are familiar with destructuring.
now, we need to add props while calling the component.
How to render components with props?
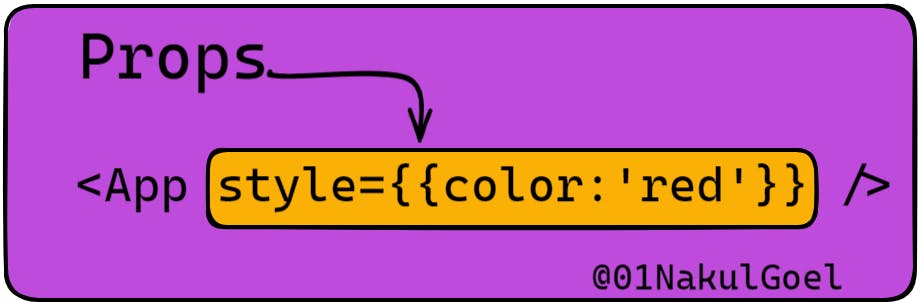
we have added all the props when we are actually calling the component
root.render(
<App style={{color:'red'}} description='I am learning React' heading='Nakul Goel' />
);
it will look like this after rendering.

we can also use objects like the below code:-
let props = {style:{color:'red'}, description:'I am learning React',heading:'Nakul Goel'}
//after that you can do destructing of props.
root.render(
<App {...props} />
);

Let us understand the component on a wider
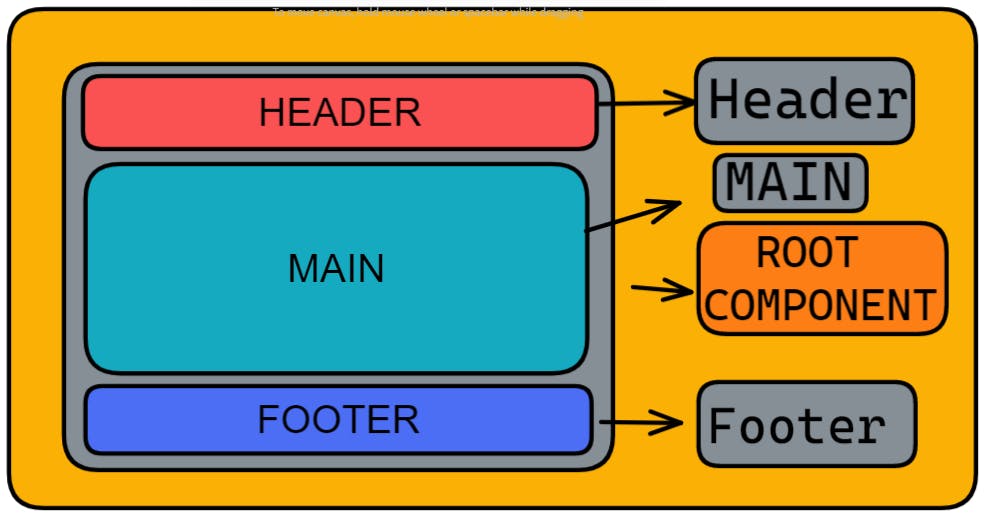
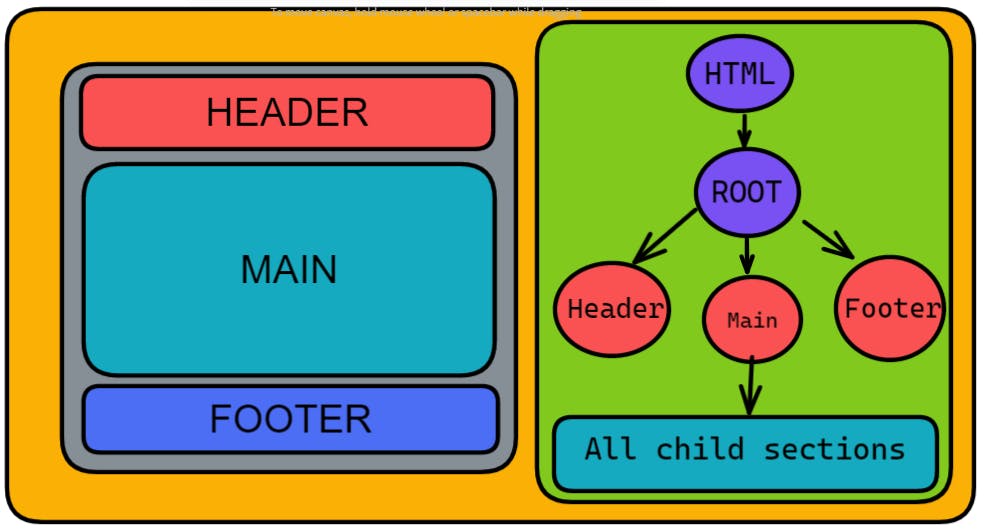
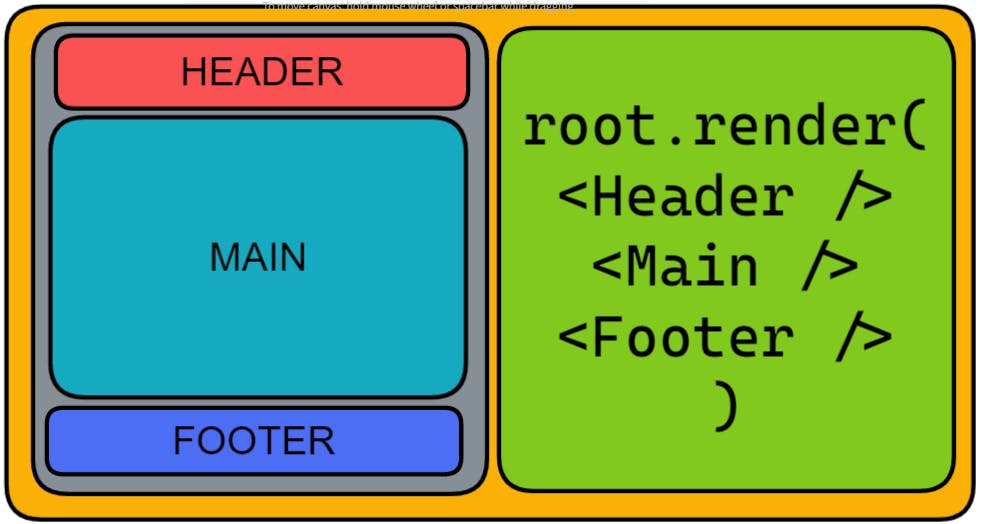
I hope this part is pretty much clear to all of you and if any one of you is facing any issue on the above diagram then comments will help you in that as well.
Activity time
Create a list of your favorite movies with JSX like this:-

open your VS code and start writing code, if you want to learn.
be honest with yourself, at last, you are learning this for your growth.
this is the code of the above problem
const App = (props) => { let { style, heading } = props; return ( <div> <h1 style={style}>{heading}</h1> <ul> <li>Black Panther (2018)</li> <li> Avengers: Endgame (2019)</li> <li> Iron Man (2008)</li> <li> Avatar: The Way of Water (2022)</li> </ul> </div> ); };this activity was simple but this activity will teach us some new things.
Activity 2.0
Psuedo code
Create a list of movies using an array of strings, where each string represents a movie in the list.
Use a map function to iterate over the array and return a list element for each item.
Use a JSX expression to enclose the list elements in a parent element, such as a div or ul element.
try it yourself give it at least five minutes on it.
we can do the above problem like this:-
const App = (props) => { let { style, heading } = props; const movies = [ "Black Panther (2018)", "Avengers: Endgame (2019)", "Iron Man (2008)", "Avatar: The Way of Water (2022)", ]; return ( <div> <h1 style={style}>{heading}</h1> <ul> { movies.map( (movie, i) => { return <li key={i}>{movie}</li>; } ) } </ul> </div> ); };here in the above code, we are running js in the curly bracket, and in that bracket, we are running a map function which is returning us an array of li tags.
[<li key=1> Black Panther (2018)</li>, <li key=2> Avengers: Endgame (2019)</li>, <li key=3> Iron Man (2008)</li>, <li key=4> Avatar: The Way of Water (2022)</li>]and when we put this array in a curly bracket it joins automatically, I will tell you one thing do not focus on how React is made only focus on how we can use it effectively.
one more new thing you must have noticed is a key attribute.
In React, the key attribute is a special attribute that is used to uniquely identify each element in a list of elements. It is often used when rendering a list of elements dynamically, such as in a map or filter function. The key attribute helps React optimize the rendering of lists by allowing it to keep track of which elements have changed, added, or removed.
make sure you always have key attributes, especially when using the map function.
const list = [ { id: 1, name: 'Item 1' }, { id: 2, name: 'Item 2' }, { id: 3, name: 'Item 3' } ]; const items = list.map(item => <li key={item.id}>{item.name}</li>); return <ul>{items}</ul>;
In this example, the key attribute is set to the id of each item in the list. This allows React to keep track of the individual items and optimize the rendering of the list. It is important to note that the key attribute should be unique within the list of elements, and should not be used for any other purpose.
useState()
In React, the state is an object that holds data relevant to a component. The state is mutable, meaning it can be changed within the component, and it causes the component to re-render when it is updated.
Here is an example of using state in a React component:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Example() {
// Declare a new state variable, which we'll call "count"
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>You clicked {count} times</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>
Click me
</button>
</div>
);
}
In this example, we use the useState hook to declare a new state variable called count, and we set its initial value to 0. We also declare a function called setCount that allows us to update the value of count.

We then use the count variable in the component's JSX, and we pass the setCount function to the onClick event of a button. When the button is clicked, the setCount function is called and the count variable is incremented by 1. This causes the component to re-render and the value of count is displayed in the component's JSX.
it can sound a lot confusing basically, useState is a hook in React that allows you to add state to functional components. It takes in a single argument, which is the initial value of the state, and returns an array with two elements: the current state value and a function that can be used to update the state.

I told you functional components are reusable in the above example you can easily see we are reusing the functional component to create three different counters.
you must be having a lot of questions in your mind, relax and work on your question yourself. still, if you are facing an issue, you can always comment, and I will help you.
Now Quiz Time
- What is a functional component in React?
A) A component that is defined as a function
B) A component that is defined as a class
C) A component that is defined as a function and cannot have state or lifecycle methods
D) A component that is defined as a class and cannot have state or lifecycle methods
- What is the main advantage of using functional components over class-based components in React?
A) Functional components are easier to understand and debug
B) Functional components are more performant
C) Functional components can have state and lifecycle methods
D) Functional components can only be used for simple components
- How do you pass data from a parent component to a functional child component?
A) By using the "props" object
B) By using the "state" object
C) By using the "context" object
D) By using the "data" object
- Can functional components have state in React?
A) Yes, by using the "useState" hook
B) No, functional components cannot have state.
C) Yes, by using the "setState" method
D) Yes, by using the "state" object
- How do you access the current state value and update the state value in a functional component using the "useState" hook?
A) By using the "this.state" and "this.setState" methods
B) By using the "state" and "setState" variables returned from the "useState" hook
C) By using the "props" and "setProps" variables returned from the "useState" hook
D) By using the "context" and "setContext" variables returned from the "useState" hook
Answers
A - A functional component is a component that is defined as a function.
B - One of the main advantages of using functional components over class-based components is that they are more performant because they do not have the overhead of managing state and lifecycle methods.
A - Data can be passed from a parent component to a functional child component using the "props" object.
A - Functional components can have state in React by using the "useState" hook.
B - The current state value and the function to update the state value in a functional component using the "useState" hook can be accessed by using the variables returned from the "useState" hook, which are "state" and "setState" respectively.
that's all for today, Merry Christmas to all of you.
keep learning, keep growing, and never stop striving to be the best developer you can be.
I will meet you in the next blog.

